Millions of people around the world love drinking coffee for its rich flavors and energy-boosting effects. Coffee also plays a key role in the world’s economy. More than 70 countries, mostly in the warm “Coffee Belt” near the equator, grow coffee. This area has the perfect weather for coffee farms, ranging from tropical to subtropical climates.
For many people, coffee isn’t just a drink to enjoy in the morning or afternoon; it’s a major part of their country’s economy. Countries that are still developing often rely on coffee as a major export. The coffee market around the world is always changing and can get pretty complicated. This is because of things like changing weather, what people want to buy, and new ways to grow and make coffee. Having so many places where coffee can grow is great for the economy and means we get to enjoy lots of different kinds of coffee. Some are smooth and balanced, like Arabica coffee, and some are strong and bold, like Robusta coffee.
When we look closer at how the world makes coffee, we see that some countries are really important for making a lot of it and adding to the coffee culture we all enjoy. Countries like Brazil, with its huge coffee farms, Colombia, with its mountainous areas, and Vietnam, with its innovative farming, all play big roles. This article will tell you more about the countries leading the way in coffee production, why they’re so good at it, and the challenges they face as things keep changing.
Which Country Produces the Most Coffee?
Brazil is known as the largest coffee producer in the world. It has held this position for over 150 years, contributing about a third of the entire coffee supply. Brazilian coffee is renowned for its variety and quality, ranging from high-grade Arabica beans to more affordable Robusta beans.
The Global Coffee Market

The world of coffee is huge and complex, connecting millions of people who grow, trade, and drink coffee all over the globe. Coffee is the second most traded item in the world, right after oil, based on how much money it’s worth. The process of getting coffee from a seed to your cup includes growing, picking, processing, exporting, roasting, and selling it, which creates lots of jobs and adds value to the economy.
Overview of the Global Coffee Market
People buy and sell coffee in a market that changes a lot. Things like the weather, whether countries are stable, and how much people want coffee can make prices go up or down. Even though prices change, more and more people, especially in new markets and younger folks who like fancy and craft coffees, want coffee.
There are two big places where people trade coffee: the New York Coffee Exchange for Arabica coffee, and the London International Financial Futures and Options Exchange for Robusta coffee. These markets help keep coffee prices more stable around the world, but local prices can still change because of things like how much coffee is made, money value changes, and other local issues.
Importance of Coffee in International Trade
Coffee is super important for trade around the world. It’s a major export for many countries in Latin America, Africa, and Asia. The money from selling coffee abroad is really important for these countries’ economies. It helps support millions of families and communities that grow and process coffee. In some places, money from coffee is a big chunk of all the money they make from selling things to other countries. This shows that coffee is not just important culturally and socially but also economically.
The Role of Coffee in the Economies of Producing Countries
In countries that grow coffee, it’s a big deal for jobs and making money. It gives work to farmers, people who pick the coffee, and those who work in processing and shipping. It also helps other parts of the economy, like transportation, making equipment, and selling coffee.
Coffee is also really important for helping rural areas develop. For many small farmers, selling coffee is the main way they make money, which they use for education, healthcare, and housing. The coffee business has also led to better infrastructure in rural areas, like roads, schools, and hospitals.
But, relying a lot on coffee can make these countries’ economies really sensitive to changes in the global coffee market. When coffee prices go up and down a lot, it can make life hard for coffee growers. Sometimes, governments have to step in with programs to help stabilize prices and support farmers.
These days, countries that grow coffee are working more on being sustainable and making better quality coffee to be more competitive globally. Efforts to improve farming methods, make sure workers are treated fairly, and reduce harm to the environment are getting more common. This is because customers want coffee that’s made in a good way, and it’s also important for the coffee business to keep doing well in the long run.
Leading Coffee-Producing Countries
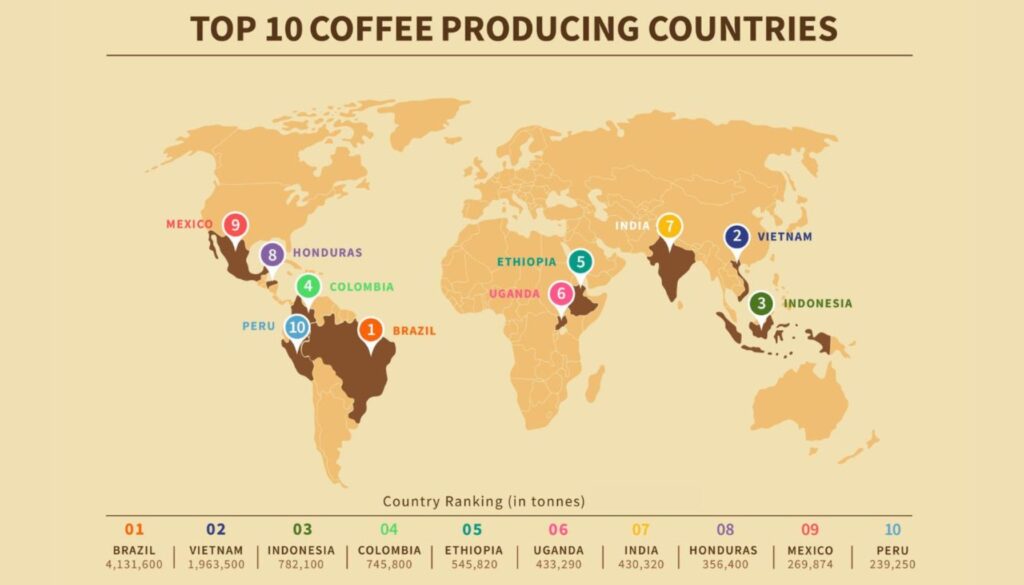
The hierarchy of coffee production is dominated by a few key players, with countries like Brazil, Vietnam, and Colombia leading the charge. These nations have honed their coffee cultivation practices over centuries, evolving to meet both the traditional and modern demands of the global market. The success of these leading coffee-producing countries can be attributed to a combination of geographical, climatic, economic, and technological factors.
Introduction to the Top Coffee-Producing Countries
- Brazil has remained the world’s largest coffee producer for over 150 years, contributing around a third of all coffee. Its vast size and variety of landscapes allow for the production of both Arabica and Robusta beans.
- Vietnam surprised the world by ascending to the second position, primarily focusing on Robusta coffee production. The country has embraced intensive farming techniques and technology to maximize output.
- Colombia is renowned for its high-quality Arabica coffee, benefiting from its ideal coffee-growing climate along the Andean mountains. It has a strong brand identity in the coffee world, emphasizing quality and sustainability.
- Ethiopia, often considered the birthplace of coffee, is the largest coffee producer in Africa. It is celebrated for its diverse coffee varieties and unique flavors, deeply intertwined with its culture.
- Indonesia and Honduras also play significant roles in the global coffee market, each bringing unique characteristics and flavors to the table.
Factors that Contribute to High Coffee Production
- Geographical and Climatic Conditions: Ideal coffee-growing conditions include temperate climates, ample rainfall, and elevation. These conditions are found in the “Coffee Belt,” which stretches between the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn. The specific climate and soil conditions in each region can affect the flavor profile of the coffee, making geography a crucial factor in coffee production.
- Agricultural Practices: Advances in agricultural techniques, including improved varietals, pest management, and cultivation methods, have significantly increased yield and quality. Countries that invest in research and development tend to see higher production volumes and better coffee quality.
- Government Policies and Support: Support from governments in the form of subsidies, research, and infrastructure development can greatly enhance a country’s coffee production capabilities. Policies that encourage sustainable practices and support smallholder farmers are particularly important in maintaining a healthy production environment.
- Market Access and Trade Relationships: Countries with better access to global markets and strong trade relationships can more easily export their coffee, driving up production to meet international demand. Trade agreements and partnerships play a key role in facilitating coffee exports.
- Investment in Technology and Infrastructure: Investment in processing facilities, transportation, and technology can improve efficiency and reduce losses, increasing the overall volume of coffee that reaches the market.
- Labor and Community Development: The social structure and labor conditions in coffee-producing regions also influence production levels. Countries that invest in their communities and ensure fair labor practices tend to have more sustainable and productive coffee industries.
The dominance of these countries in the coffee sector is not just a result of their geographical luck but also their ability to adapt to market demands, innovate, and invest in the future of coffee production. Each leading coffee-producing country has carved out its niche, contributing to the rich diversity of the global coffee culture.
Brazil: The Coffee Giant

Brazil’s status as the world’s leading coffee producer is not just a testament to its vast agricultural lands but also to its centuries-long dedication to the crop. The country has developed an expansive and efficient coffee industry that is unrivaled in terms of volume, diversity, and innovation.
Overview of Brazil’s Coffee Industry
Brazil accounts for about one-third of all coffee produced worldwide, making it the largest coffee producer on the globe. The coffee industry plays a crucial role in Brazil’s economy, not only in terms of export revenues but also as a major employer in the rural sector. Brazilian coffee farms range from small, family-run operations to large, mechanized estates, allowing for a wide variety of production methods and coffee types.
Historical Context of Coffee Production in Brazil
Coffee was introduced to Brazil in the early 18th century and quickly became a dominant crop in the country’s southeast regions. By the 19th century, Brazil had ascended to the top of the global coffee market, a position it has maintained with few interruptions ever since. The coffee industry has played a critical role in shaping Brazil’s social and economic landscape, contributing to urbanization and the development of infrastructure.
Geographic and Climatic Conditions Favorable for Coffee Production
Brazil’s supremacy in coffee production can be largely attributed to its ideal geographic and climatic conditions. The country’s vast size encompasses diverse landscapes, including the Brazilian Highlands which offer perfect conditions for coffee cultivation: altitude, a tropical climate with a well-defined wet and dry season, and fertile soil. These conditions are particularly favorable for Arabica beans, which are prized for their mild, nuanced flavors and make up the majority of Brazil’s coffee production.
Types of Coffee Produced
While Brazil is famous for its high-quality Arabica coffee, it also produces Robusta coffee, especially in the regions where the climate is hotter and more humid. The country’s diverse climate and geography allow for a wide range of coffee varieties, each with its own unique profile, including Bourbon, Typica, Caturra, and Mundo Novo.
Challenges Faced by the Brazilian Coffee Industry
Despite its success, the Brazilian coffee industry faces several significant challenges:
- Climate Change: Altering weather patterns, including unpredictable rainfall and temperature increases, threaten coffee production, especially the more temperature-sensitive Arabica variety.
- Pests and Diseases: The coffee borer beetle and leaf rust are among the pests and diseases that can devastate crops, requiring constant vigilance and innovation in pest management techniques.
- Labor Issues: The coffee industry relies heavily on manual labor, especially during the harvest season. Issues such as labor shortages, fair wages, and working conditions are ongoing concerns.
- Market Volatility: Global coffee prices are highly volatile, subject to changes in global supply and demand. This can impact farmers’ incomes and make long-term planning difficult.
- Environmental Concerns: Sustainable farming practices are increasingly important to consumers. The industry faces pressure to reduce deforestation, water use, and chemical inputs, and to improve soil health and biodiversity.
In response to these challenges, Brazil continues to invest in research and development, sustainable practices, and technological innovations, striving to maintain its position as the world’s coffee powerhouse while ensuring the future viability of its coffee industry.
Vietnam: A Robust Competitor

Vietnam’s ascent in the coffee industry is a remarkable success story of the late 20th and early 21st centuries. From a relatively modest beginning in coffee production, Vietnam has rapidly become the world’s second-largest coffee producer, specializing in Robusta coffee. This growth has been fueled by a combination of government policy, entrepreneurial spirit, and the adaptation of innovative agricultural techniques.
Overview of Vietnam’s Rise in the Coffee Industry
Vietnam’s coffee industry began to take off in the 1980s, following economic reforms that encouraged private enterprise and investment in agriculture. The government identified coffee as a strategic crop that could help transform the country’s economy, particularly in the Central Highlands region, which offered ideal conditions for growing coffee. Through concerted efforts, including the allocation of land for coffee plantations and investment in infrastructure, Vietnam quickly escalated its position in the global coffee market.
The Dominance of Robusta Coffee
Unlike Brazil, which is renowned for its Arabica production, Vietnam has focused on Robusta coffee, a variety that thrives in its climate and soil. Robusta beans are more bitter and contain higher caffeine levels than Arabica, making them suitable for espresso blends and instant coffee. Vietnam’s dominance in Robusta production has made it a key player in the global coffee market, particularly in segments where Robusta is preferred.
Innovations and Advancements in Production Techniques
Vietnam’s meteoric rise in coffee production is also a result of embracing innovations and advancements in farming techniques. Intensive farming practices, the use of high-yield varieties, and irrigation technology have significantly increased productivity. Moreover, Vietnam has invested in processing infrastructure, improving the quality and marketability of its coffee products. The adoption of direct trade and fair trade practices has also opened new markets, especially in the West, where there’s a growing demand for sustainably sourced coffee.
Challenges and Environmental Concerns
Despite its success, the Vietnamese coffee industry faces several challenges:
- Environmental Impact: The rapid expansion of coffee plantations has led to deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and soil degradation in some areas. Intensive farming practices have raised concerns about water usage and pollution.
- Climate Change: Like other coffee-producing countries, Vietnam is vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, with increasing risks of unpredictable weather patterns, pests, and diseases.
- Economic Sustainability: The fluctuating prices of coffee on the global market can impact farmers significantly, many of whom are smallholders. The reliance on a single crop also makes them vulnerable to market and environmental changes.
- Quality Improvement: While known for its Robusta production, Vietnam has been working to improve the quality of its coffee and expand into the specialty coffee market. This requires ongoing investment in training and technology.
In response to these challenges, there’s a growing emphasis on sustainable agriculture practices within the Vietnamese coffee industry. Efforts to promote agroforestry, reduce chemical use, and improve water management are underway, aiming to ensure the long-term viability of Vietnam’s coffee sector. The country is also exploring the cultivation of higher-quality Robusta and Arabica varieties to diversify its offerings and tap into new markets.
Colombia: Quality Over Quantity

Colombia holds a prestigious position in the global coffee market, renowned not just for the volume of coffee it produces but for the exceptional quality of its beans. Colombian coffee is often associated with a rich, mild flavor and a balance of acidity and sweetness that appeals to a wide range of palates. The country’s focus on quality over quantity has set Colombian coffee apart, establishing it as a favorite among coffee aficionados worldwide.
The Role of Colombia in the Global Coffee Market
Colombia is the third-largest producer of coffee in the world and the largest producer of washed Arabica coffee. Its reputation for high-quality coffee has been carefully cultivated, supported by the Colombian Coffee Growers Federation (FNC), a powerful and influential organization that has been instrumental in promoting Colombian coffee on the global stage. The FNC’s marketing efforts, including the iconic Juan Valdez character, have helped Colombian coffee to command higher prices in international markets.
Geographic Advantages for Arabica Production
Colombia’s geography offers unique advantages for the production of Arabica coffee. The country’s location along the equatorial belt, combined with its varied topography, results in a wide range of microclimates. These conditions are ideal for Arabica coffee, which prefers cooler temperatures and higher elevations. The Andean mountains, in particular, provide the perfect environment for coffee cultivation, with their rich volcanic soil and consistent climate.
Initiatives for Sustainable and High-Quality Coffee Production
Recognizing the importance of sustainability in coffee production, Colombian producers and the FNC have implemented numerous initiatives aimed at improving both the quality of coffee and the livelihoods of coffee growers. These initiatives include:
- Coffee certification programs, such as Rainforest Alliance, UTZ Certified, and Fair Trade, which encourage sustainable farming practices and ensure fair compensation for farmers.
- Research and development into disease-resistant and higher-yield coffee varieties to combat the challenges posed by climate change and pests, while maintaining the unique flavors of Colombian coffee.
- Education and support for coffee farmers, including training in best agricultural practices, access to financing, and assistance in improving farm management and processing techniques to enhance coffee quality.
Challenges Facing Colombian Coffee Producers
Despite its success, the Colombian coffee industry faces several challenges:
- Climate Change: Increasingly unpredictable weather patterns, including excessive rainfall and droughts, threaten coffee production, making it harder for farmers to maintain consistent quality and yields.
- Rising Production Costs: High labor costs and the need for investment in sustainable practices and infrastructure pose financial challenges for smallholder farmers, who make up the majority of coffee producers in Colombia.
- Market Volatility: Fluctuations in global coffee prices can significantly affect farmers’ incomes, making it difficult for them to invest in improvements or sometimes even cover production costs.
Colombia’s approach to coffee production, with its emphasis on quality and sustainability, has set a standard in the global coffee market. By continuing to innovate and adapt to the challenges it faces, Colombia aims to secure its place as a leader in the production of high-quality coffee, supporting its economy and the millions of people who depend on the coffee industry for their livelihoods.
Ethiopia: Birthplace of Coffee

Ethiopia holds a special place in the world of coffee not only as a major producer but as the birthplace of the coffee plant itself. The story of coffee is deeply woven into Ethiopian culture, and the country’s production methods have remained largely traditional, reflecting a deep respect for the crop’s heritage.
Historical Significance and Traditional Production Methods
Legend has it that coffee was discovered in Ethiopia by a goat herder named Kaldi, who noticed his goats frolicking energetically after eating the red cherries from a certain tree. This story, though apocryphal, symbolizes Ethiopia’s long-standing connection with coffee. Ethiopian coffee production is characterized by its traditional methods, where coffee is often grown in small gardens or forested areas, using organic farming practices passed down through generations. The coffee is typically sun-dried and processed using natural methods that preserve its unique flavors.
Types of Coffee and Regions of Production
Ethiopia is known for its wide variety of coffee flavors, which vary significantly by region due to the diverse microclimates and soil conditions:
- Sidamo produces coffee with citrus and floral notes.
- Yirgacheffe, a sub-region of Sidamo, is famed for its aromatic and mild coffees with bright acidity.
- Harrar offers coffee with a strong body, spicy flavors, and hints of fruity wine.
- Limu coffees are known for their balanced body and sweet, spicy flavors.
Each region’s unique coffee profile is a testament to Ethiopia’s rich biodiversity and traditional farming practices.
Indonesia: A Diverse Producer

Indonesia’s archipelago offers a broad diversity of microclimates and landscapes, making it one of the world’s most diverse coffee-producing countries. The country’s coffee production is characterized by its wide range of flavors and processing methods, influenced by its varied geography.
Variety of Coffee Types and Production Methods
Indonesian coffee production is notable for its heterogeneity, with each island contributing its distinct coffee type:
- Sumatra is famous for its full-bodied, earthy coffees with complex flavors, often processed using the wet-hulling method, which gives the coffee its unique characteristics.
- Java, one of the earliest coffee-producing regions, offers a clean, sweet cup with a somewhat floral note.
- Sulawesi (formerly Celebes) produces coffee with a rich, full body and vibrant, spicy notes.
- Bali and Flores are known for their sweet, soft coffees with a slight floral and chocolate undertone.
These diverse profiles are a result of Indonesia’s wide range of climatic conditions and innovative processing methods, including wet-hulling, a process unique to Indonesia that impacts the coffee’s final flavor profile.
Challenges of Island Production and Climate Change
Producing coffee on an archipelago presents unique challenges, including logistical issues related to transportation and export, as well as vulnerability to climate change. The effects of climate change, such as rising temperatures, shifting rainfall patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events, pose significant risks to coffee production across Indonesia’s islands. These challenges are compounded by the need to maintain sustainable farming practices in sensitive island ecosystems, where the balance between agriculture and environmental conservation is critical.
Both Ethiopia and Indonesia contribute significantly to the global coffee culture, offering unique coffees that reflect their rich histories, diverse cultures, and innovative production methods. Despite facing distinct challenges, including those posed by climate change and market dynamics, these countries continue to adapt and thrive, ensuring their place in the world’s coffee heritage.
Factors Influencing Coffee Production

Coffee production is influenced by a myriad of factors that interplay to shape the quality, quantity, and sustainability of the coffee market. These factors range from the climatic conditions crucial for coffee growing to the technological advancements that enhance farming and processing methods, as well as broader economic and environmental considerations.
Climatic Conditions and Their Impact on Coffee Quality and Quantity
The quality and quantity of coffee production are heavily dependent on climatic conditions. Coffee plants require specific temperatures, rainfall patterns, and altitudes to flourish. For instance, Arabica coffee, which is prized for its flavor, typically grows best at altitudes between 600 and 2,200 meters in temperatures ranging from 15 to 24°C, while Robusta coffee prefers lower altitudes and warmer temperatures.
Climate change poses significant challenges to coffee production, with rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events, such as droughts and heavy rainfall. These changes can lead to reduced yields, increased vulnerability to pests and diseases, and shifting of coffee-growing areas, which can affect the quality and quantity of coffee produced.
Technological Advancements in Coffee Farming and Processing
Technological advancements have significantly impacted coffee farming and processing, leading to increased efficiency, improved quality, and reduced environmental impact. Innovations include precision agriculture techniques, such as drone and satellite imaging for monitoring crop health and soil moisture levels, and the development of disease-resistant coffee plant varieties through genetic research.
In processing, new methods like the wet fermentation process and mechanical drying have improved the consistency and flavor profile of coffee beans. Moreover, advancements in packaging and transportation technologies help to preserve the quality of coffee as it moves from farms to consumers around the world.
Economic Factors and Global Market Trends
The global coffee market is influenced by a variety of economic factors, including supply and demand dynamics, price volatility, and trade policies. The price of coffee on the international market can fluctuate widely due to changes in production levels, affected by climate conditions or political instability in producing countries, as well as shifts in consumer demand, such as the growing preference for specialty coffees.
Economic sustainability is also a significant concern, with many coffee farmers facing challenges related to low market prices, high production costs, and limited access to credit and markets. Initiatives like direct trade and fair trade aim to improve economic outcomes for coffee producers by offering better prices and more stable purchasing agreements.
Environmental Sustainability and Ethical Concerns
Sustainability and ethical considerations are increasingly important in the coffee industry. There is growing awareness of the need for environmentally friendly farming practices that conserve water, preserve biodiversity, and reduce the use of harmful chemicals. Sustainable certifications, such as Rainforest Alliance and Organic, help consumers identify coffees produced under these conditions.
Ethical concerns also extend to labor practices in the coffee industry. Issues such as fair wages, safe working conditions, and child labor are critical, with various certification programs and initiatives in place to address these challenges and promote social responsibility within the coffee supply chain.
The interplay of these factors—climatic conditions, technological advancements, economic dynamics, and sustainability concerns—will continue to shape the future of coffee production. Adapting to these influences is crucial for the coffee industry to ensure resilience, sustainability, and the continued enjoyment of coffee by consumers worldwide.
The Future of Coffee Production

The future of coffee production is poised at a critical juncture, facing both challenges and opportunities. Climate change, technological innovations, and the emergence of new coffee-producing regions will significantly influence the direction of the global coffee industry.
Potential Shifts in Global Production Due to Climate Change
Climate change is expected to have profound effects on coffee production, potentially leading to shifts in global production patterns. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns can make traditional coffee-growing areas less suitable for cultivation, especially for Arabica coffee, which is sensitive to temperature increases. This could result in a geographic shift of coffee farming to higher altitudes or to regions that were previously unsuitable, affecting the global distribution of coffee production.
Moreover, climate change may exacerbate challenges related to pests and diseases, such as coffee leaf rust and the coffee berry borer, which could further impact yields and quality. Adaptation and mitigation strategies, such as developing resistant coffee plant varieties, implementing agroforestry systems, and optimizing water use, will be critical in responding to these challenges.
Technological Innovations and Their Impact on Production and Sustainability
Technological innovations hold the promise of transforming coffee production, making it more efficient, sustainable, and resilient. Precision agriculture technologies, including drones, IoT sensors, and satellite imaging, can optimize resource use and improve crop health monitoring, leading to increased yields and reduced environmental impact.
Advancements in genetic research may produce coffee plant varieties that are not only resistant to pests and diseases but also adaptable to changing climatic conditions, preserving quality and flavor profiles. Furthermore, innovations in processing, packaging, and logistics can enhance the efficiency of the coffee supply chain, reduce waste, and maintain the quality of coffee from farm to cup.
Emerging Coffee Producers and Markets
The global coffee landscape is also being reshaped by the emergence of new coffee producers and markets. Countries in Africa, Asia, and Latin America that have not traditionally been major players in the coffee industry are beginning to gain recognition for their unique coffee profiles and sustainable farming practices. For example, countries like China, Myanmar, and Laos are investing in coffee production and starting to export high-quality beans to international markets.
The expansion of coffee culture in producing countries, often referred to as the “third wave” of coffee, is creating new domestic markets for specialty coffees. This trend is fostering a closer connection between producers and consumers, encouraging innovation in coffee production and processing methods, and emphasizing quality, sustainability, and traceability.
The future of coffee production will undoubtedly be shaped by how the industry addresses the challenges posed by climate change, leverages technological advancements, and embraces the opportunities presented by emerging coffee producers and markets. Adapting to these changes will require concerted efforts from all stakeholders in the coffee value chain, from farmers and researchers to businesses and consumers, to ensure the sustainability and resilience of the global coffee industry.
Conclusion
Learning about how different countries produce coffee is really important for a few reasons. It shows us the variety of farming methods, weather conditions, and economic situations that make up the world of coffee. Every country that grows coffee adds its own special taste and quality to the coffee we drink, showing off the culture and natural diversity of its area. It’s key to understand these differences to fully appreciate coffee’s complexity and value worldwide.
Coffee is super important for the world’s economy. It’s one of the top agricultural products that people trade, and it’s essential for the income of millions of people, especially in countries that are still developing. The coffee business helps with global trade, supports the development of rural areas, and encourages countries to work together.
Looking into the future, the coffee industry might see some big changes. Climate change could really challenge the usual places where coffee grows, which might make us rethink how and where we grow coffee. New technologies could help make coffee farming more sustainable and productive, helping the industry keep up with new problems. Also, new coffee-growing countries and changing tastes among coffee drinkers might change the market, especially with more people wanting special kinds of coffee, sustainable options, and products where they know where the coffee came from.
The story of how coffee gets from the farm to your cup involves a lot of different factors – like the environment, the economy, and society. As the coffee world faces 21st-century challenges and opportunities, working together—producers, drinkers, researchers, and government officials—will be really important. This teamwork can help make sure coffee stays a favorite drink and a key part of the world’s economy, making life better for people everywhere.
References and Further Reading
- Nescafé. (n.d.). Coffee producing countries. Retrieved from https://www.nescafe.com/gb/coffee-culture/knowledge/coffee-producing-countries
- Visual Capitalist. (n.d.). The world’s top coffee producing countries. Retrieved from https://www.visualcapitalist.com/worlds-top-coffee-producing-countries/
- National Coffee Association USA. (n.d.). Coffee around the world. Retrieved from https://www.ncausa.org/About-Coffee/Coffee-Around-the-World






